[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Zirconium Powder: Superior Quality for Your Applications
Discover excellence in zirconium powder at ARS METAL. We lead the industry, crafting top-quality powder with precision. Our focus on cutting-edge methods ensures a product that outshines the rest.
What sets us apart? Rigorous quality checks and customization options tailored to your needs. Our powder excels in a variety of applications, showcasing its versatility and performance across different fields. Each particle is a testament to our commitment to perfection.
At ARS METAL, we’re not just suppliers; we’re reliable partners in your projects’ success. Explore innovation and reliability in every particle. Choose a zirconium powder manufacturer that stands out—choose us.
What is Zirconium Powder
Zirconium powder is zirconium metal in grey powder form. It is a finely milled substance composed of zirconium particles, known for its exceptional purity and precision. This powdery form of zirconium is crafted through advanced manufacturing processes, ensuring a high-quality product with diverse applications across various industries.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
Zirconium Powder Specifications
| Atomic Number | 40 |
|---|---|
| Liquid Density at M.P. | 5.8 g/cm³ |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol.) | 91.22 |
| Apparent Density @25°C (g/cm3) | 6.506 |
| Specific Heat @25°C (cal/g-°C) | 0.066 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 1852 |
| Boiling Point (°C) | ~ 3580 |
| Thermal Conductivity (cal/s-cm-°C) | 0.0505 |
| Vickers Hardness | 110 |
| Surface Area (m2/g) | |
| Crystallography | Hexagonal structure |
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
Chemical Composition of Zirconium Powder
| Grade | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr+Hf | H | O | N | C | Fe | |
| ≥ | ≤ | |||||
| Zr | 99.5 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 0.042 |
| Zr-4 | – | 0.005 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.24 |
| Sieve Mesh | -60mesh – +400mesh 1-3um, D50=0.5um |
|||||
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
| Grade | Total Zr<% | Active Zr% | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Ca | Mg | Al | S | Cl | F | Flash Point | |||
| FZrb-11 | 92.0 | 70-80 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 280-370 |
| FZrb-12 | 270-350 | |||||||||
| FZrb-13 | 260-330 | |||||||||
| FZrb-21 | 95.0 | ≥90 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 270-340 |
| FZrb-22 | 250-330 | |||||||||
| FZrb-23 | 220-320 | |||||||||
| FZrb-1 | 96.0 | ≥90 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.008 |
200-280 |
| FZrb-2 | 96.0 | ≥92 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 0.008 |
200-280 |
| Grade | Standart Sieve Mesh (um) | Size | Average Size (um) | |||||||
| <6um | <10um | 10-20um | >20um | |||||||
| FZrb-11 | 63 | – | 17-27 | 28-43 | 35-50 | 18±3 | ||||
| FZrb-12 | 63 | – | 34-45 | 25-40 | 15-30 | 13±3 | ||||
| FZrb-13 | 63 | – | 50-70 | 28-43 | <10 | 9±2 | ||||
| FZrb-21 | 63 | – | 17-27 | 28-43 | 35-50 | 13±3 | ||||
| FZrb-22 | 63 | – | 35-45 | 25-40 | 15-30 | 13±2 | ||||
| FZrb-23 | 63 | – | 50-70 | 28-43 | <10 | 9±2 | ||||
| FZrb-1 | 45 | ≥80 | – | – | – | 6±2 | ||||
| FZrb-2 | 45 | ≥90 | – | – | – | 6±2 | ||||
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Why Choose ARS METAL Zirconium Powder?
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
Supreme Purity and Precision
Our zirconium powder boasts exceptional purity. It is crafted for precision in every application.
Tailored Solutions for Your Unique Needs
Tailor the particle sizes to your specifications, offering a personalized solution for unique project requirements, and showcasing effectiveness in diverse applications.
Consultative Partnership
Our team provides expert consultations, guiding you through the optimal use of our zirconium powder, establishing a reliable and collaborative partnership.
Stringent Quality Control
Rigorous quality checks at every stage of manufacturing guarantee a consistently high-quality product.
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
We employ cutting-edge manufacturing methods to craft zirconium powder, staying at the forefront of industry advancements.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][vc_custom_heading text=”How is Zirconium Powder Made
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]
Metal Thermal Reduction Method
The metal thermal reduction method utilizes the reaction of metal reducing agents with metal oxides or chlorides to prepare metals.
1. Calcium Reduction Method
Calcium reduces zirconium oxide to produce zirconium powder. ZrO2 is used as raw material, and pure metallic calcium is the reducing agent. The process involves mixing, sealing, vacuuming, and filling with argon. Then, the mixture is reduced at a temperature of 1000℃~1100℃. The reactant is a mixture of zirconium powder, calcium chloride, calcium oxide and excess calcium. The zirconium powder can be obtained by leaching it with hydrochloric acid. Then wash, crush, filter, dry, and screen it.
2. Calcium Hydride Reduction Method
To produce zirconium powder by reducing zirconium oxide with calcium hydride, first hydrogenate calcium and grind it into powder. Then, mix it with ZrO2, and reduce it at 1000℃~1100℃. The reaction product is a mixture of zirconium powder containing a small amount of hydrogen, calcium oxide, and a little excess calcium. Zirconium powder can be obtained by washing, grinding, screening and drying.
3.Sodium Reduction Method
The method for producing zirconium powder by sodium reduction of potassium zirconofluorate is to use K2ZrF6 as raw material. An appropriate amount of potassium chloride and sodium chloride molten salt is added. Then, the mixture is reduced at about 860°C. After that, the zirconium powder is obtained. It’s obtained by acid leaching, washing, grinding, and drying the reaction product.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]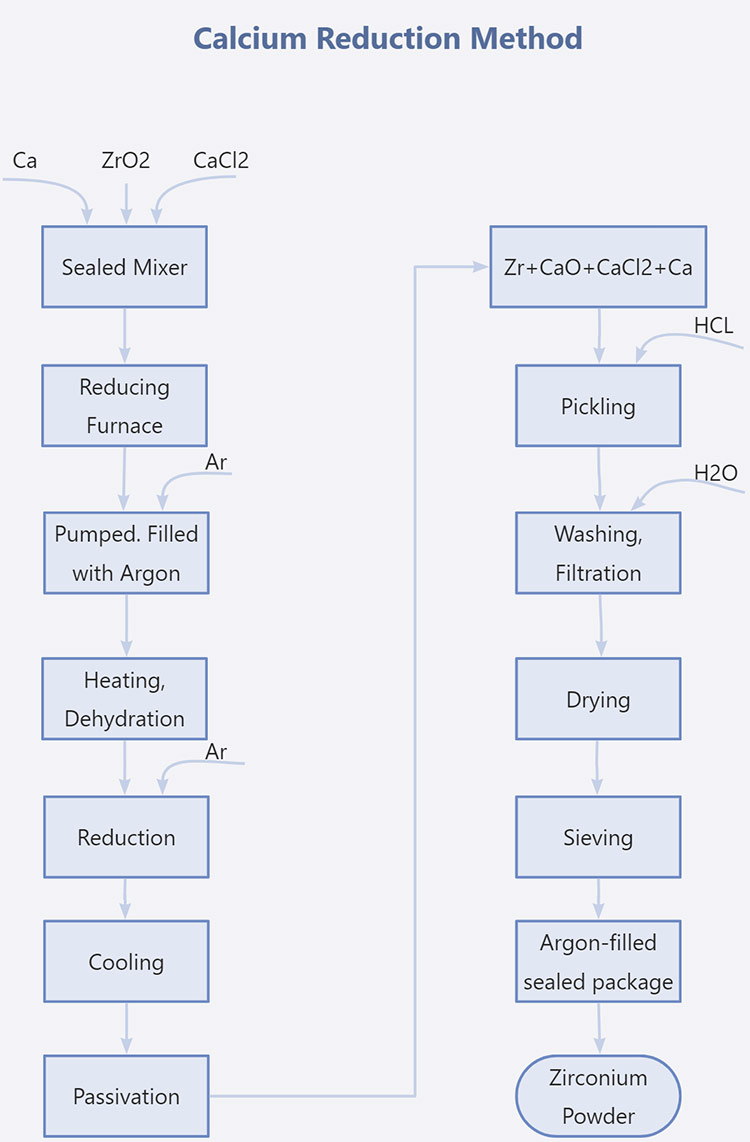 [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
Molten Salt Electrolysis
The electrolysis method uses potassium fluorozirconate and sodium chloride as raw materials. We dry them, heat and melt them, and insert them into the cathode for electrolysis. After electrolysis, zirconium is deposited on the cathode in the form of powder. The sediment is taken out, crushed, washed with water, washed with ethanol, and dried to obtain a purity of 99% high purity zirconium powder.[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text css=””]
Hydrodehydrogenation
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]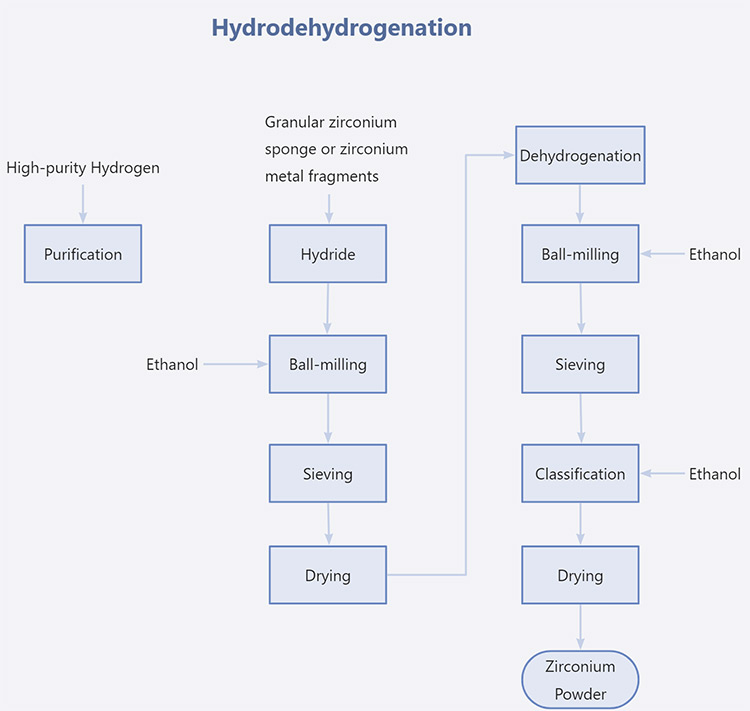 [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]The hydrodehydrogenation method uses sponge zirconium or electrolytic zirconium as raw materials. During production, zirconium sponge is broken into particles (metal is cut into chips). Then, it is hydrogenated at 600°C to 700°C to make zirconium hydride. Zirconium hydride is crushed and dried. Then, it is put into a furnace and dehydrogenated at a temperature of 600°C~900°C to obtain zirconium powder.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Strict Quality Control of Zirconium Powder
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]The hydrodehydrogenation method uses sponge zirconium or electrolytic zirconium as raw materials. During production, zirconium sponge is broken into particles (metal is cut into chips). Then, it is hydrogenated at 600°C to 700°C to make zirconium hydride. Zirconium hydride is crushed and dried. Then, it is put into a furnace and dehydrogenated at a temperature of 600°C~900°C to obtain zirconium powder.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Strict Quality Control of Zirconium Powder
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF):
XRF is a non-destructive technique. It analyzes the elemental composition of zirconium powder. It helps determine the presence of impurities. It ensures that the desired zirconium concentration is achieved.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS):
ICP-MS is a highly sensitive method. It quantifies the elemental composition of zirconium powder. It can detect trace elements and impurities. This provides precise information about the material’s purity.
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD):
XRD is used to examine the crystal structure of zirconium powder. It confirms the presence of the desired zirconium phases. It also identifies any unwanted crystalline structures that may affect the material’s properties.
Particle Size Analysis:
Measuring the particle size distribution is crucial for zirconium powder quality. Techniques such as laser diffraction or sedimentation are employed to ensure that the powder meets specified size requirements. This is essential for various applications.
Chemical Analysis:
Conducting chemical analyses, including wet chemical methods, allows for a detailed examination of the chemical composition of zirconium powder. This method aids in confirming the absence of impurities and verifying the material’s purity.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””] [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Where Our Zirconium Powder Shines-Diverse Applications
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Where Our Zirconium Powder Shines-Diverse Applications
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Nuclear Energy
Zirconium powder can be used as nuclear fuel rod material in reactors of nuclear power plants. Zirconium powder has excellent nuclear industry properties such as high melting point and low neutron absorption cross-section, which can effectively ensure the stability and safety of nuclear fuel rods.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Aerospace Industry
Zirconium powder is mainly used to manufacture high-temperature alloys and corrosion-resistant materials. These materials can be used for components in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, such as rocket engines, aircraft engines and missiles, as well as corrosion-resistant materials in marine environments, such as ships.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Ceramics Industry
Due to the high melting point and low thermal conductivity of zirconium powder, the ceramic products made of zirconium powder can withstand high-temperature erosion, and have extremely high abrasion and corrosion resistance. Ceramic products made of zirconium powder can be used to manufacture refractory materials, cutting tools, abrasives and so on.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Chemical Industry
Zirconium powder can be used as catalyst carrier, reactor material and anti-corrosion material. Among them, catalyst carriers are mainly used in fine chemicals, petrochemicals, environmental protection and other fields, reactor materials are mainly used for chemical reactor linings and seals, and anti-corrosion materials are mainly used for anti-corrosion coatings in chemical equipment, marine equipment and other environments.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Jewelry Industry
Zirconium powder is utilized in the jewelry industry to create zirconia, a diamond substitute known for its hardness and brilliance. Zirconia is also used for creating colorful, durable, and cost-effective coatings on jewelry.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_column_text css=””]
Electronic industry
Zirconium powder can be used as materials for electronic components, such as capacitors, resistors, inductors and so on. Zirconium powder has excellent electrical properties such as high melting point and low resistivity, which can meet the high requirements of electronic components on materials.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][vc_custom_heading text=”How Zirconium Powder Outperforms Its Competitors
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]
Advantages of Titanium Powder
Corrosion Resistance: Zirconium exhibits superior corrosion resistance. It is preferable for applications where exposure to harsh environments is a concern.
Lower Density: Zirconium has a lower density than titanium. This could provide weight advantages in applications where weight is a critical factor.
Advantages of Aluminum Powder
Higher Melting Point: Zirconium has a higher melting point than aluminum. This makes it suitable for applications that involve high temperatures.
Chemical Inertness: Zirconium is more chemically inert than aluminum. This makes it a better choice in certain chemical and industrial processes.
Advantages of Hafnium Powder
Availability: Zirconium is more abundant and cost-effective compared to hafnium. This makes it a more accessible choice for many applications.
Compatibility: Zirconium is more compatible with certain alloys. It is more commonly used in metallurgical applications.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=””]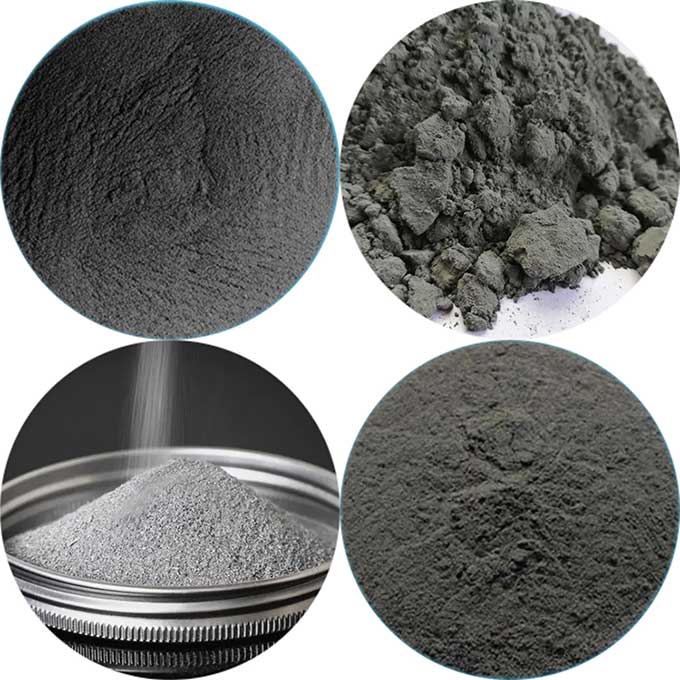 [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][vc_custom_heading text=”Zirconium Powder Package
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space][vc_custom_heading text=”Zirconium Powder Package
” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” css=””][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=””]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]