Tungsten Powder
Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten Oxide Powder
Tungsten Copper Alloy
Silver Tungsten Alloy
Tungsten Bar
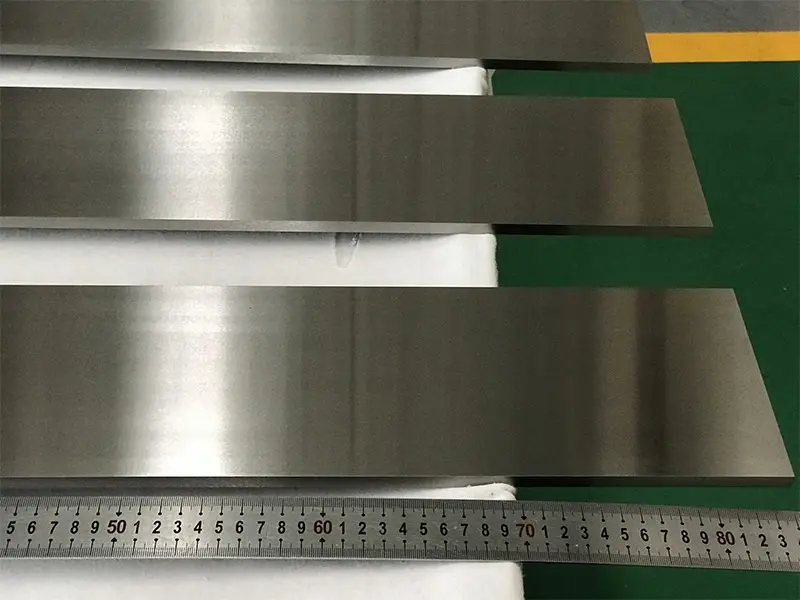
Premium Tungsten Supplier
- Your Source for High-Quality Tungsten
Tungsten is a metal known for its exceptional properties. It has the highest melting point (3422°C), lowest vapor pressure, and highest tensile strength among all metals. It also has a very high density (19.3g/cc), and a high degree of mechanical strength and ductility. These qualities make it a great option for applications that need to withstand high temperatures, remain stable in shape, and have strong mechanical strength.
ARS Metal is a professional tungsten supplier, we provide a variety of tungsten products, including pure tungsten metals, tungsten heavy alloys, tungsten copper, tungsten silver, and tungsten carbide. Our products are of high quality and competitively priced. If you need custom products, feel free to reach out to us.
The Standards of Tungsten Products
- ASTM B760/B760M – Standard Specification for Tungsten Plate, Sheet, and Foil
- ASTM B777 – Standard Specification for Tungsten Base, High-Density Metal
- ASTM B708 – Standard Specification for Tungsten-Rhenium Alloy Plate, Sheet, and Foil
- ASTM B521 – Standard Specification for Tungsten and Tungsten Alloy Wire
-
 Spherical Tungsten Powder
Spherical Tungsten Powder -
 Cemented Tungsten Carbide
Cemented Tungsten Carbide -
 Tungsten Narrow Band
Tungsten Narrow Band -
 Tungsten Rhenium Alloy
Tungsten Rhenium Alloy -
 Tungsten Wire
Tungsten Wire -
 Tungsten Tube
Tungsten Tube -
 Tungsten Sputtering Target
Tungsten Sputtering Target -
 Tungsten Sheet
Tungsten Sheet -
 Tungsten Rod
Tungsten Rod -
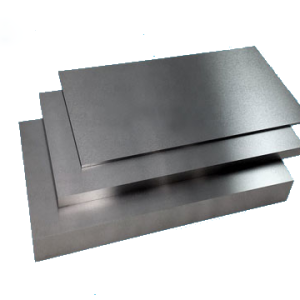 Tungsten Plate
Tungsten Plate -
 Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WNiFe, WNiCu, WNiCo)
Tungsten Heavy Alloy (WNiFe, WNiCu, WNiCo) -
 Tungsten Heating Elements
Tungsten Heating Elements -
 Tungsten Electrode
Tungsten Electrode -
 Tungsten Crucible
Tungsten Crucible -
 Tungsten Boat
Tungsten Boat -
 Tungsten Bar
Tungsten Bar -
 Silver Tungsten Alloy
Silver Tungsten Alloy -
 Tungsten Copper Alloy
Tungsten Copper Alloy -
 Tungsten Oxide Powder
Tungsten Oxide Powder -
 Tungsten Carbide Powder
Tungsten Carbide Powder -
 TUNGSTEN POWDER
TUNGSTEN POWDER
Physical Properties of Tungsten
| Density | lb/in3 | 0.7 |
| gm/cm3 | 19.27 | |
| Melting Point | °F | 6170 |
| °C | 3410 | |
| Thermal Conductivity | Cal/cm2/cm°C/sec | 0.48 |
| Specific Heat | Cal/gm/°C | 0.032 |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | micro-in/°F x 10-6 | 4.3 |
| micro-in/°C x 10-6 | 2.4 | |
| Electrical Resistivity | micro-ohm-cm | 5.5 |
Mechanical Properties of Tungsten
| Tensile Strength | KSI (Mpa)-RT | 250 (1725) |
| KSI (Mpa)-500°C | 150 (1035) | |
| KSI (Mpa)-1000°C | 75 (515) | |
| Elongation | % in 1.0″. | — |
| Hardness | DPH | 300 |
| Modulus of Elasticity | KSI | 58000 |
| Gpa | 400 |
Applications of Tungsten
Electronics & Electrical Devices

Tungsten is used in the production of electronic components, such as filaments in light bulbs and cathodes in vacuum tubes.
Tungsten alloys are used in the manufacturing of contacts and electrodes for electrical switches and relays.
Mining & Drilling

Tungsten carbide, a compound of tungsten and carbon, is widely used in the mining and drilling industries for cutting tools, drill bits, and other wear-resistant applications.
Aerospace & Defense

Tungsten alloys are employed in the aerospace industry for the production of high-performance components like rocket nozzles, balance weights, and rotor blades.
Tungsten is used in the defense industry for armor-penetrating projectiles and as a component in various military applications.
Automotive Industry

Tungsten carbide is used to produce hard-wearing components for the automotive industry, including cutting tools and wear-resistant parts.
Manufacturing & Metalworking

Tungsten and tungsten alloys are used in the production of high-speed tools, such as cutting tools, milling cutters, and drills.
Tungsten is used as a material for resistance welding electrodes.
Medical Devices
Tungsten is used in medical applications for X-ray tubes, radiation shielding, and collimators. Tungsten alloys are used in radiation therapy for cancer treatment due to their high density and radiation-absorbing properties.
Nuclear Applications
TTungsten is used in nuclear reactors and as a radiation shield due to its high density and ability to absorb radiation.
Tungsten alloys are used in the production of collimators and shielding materials for nuclear medicine.
Electrodes and Arc Welding
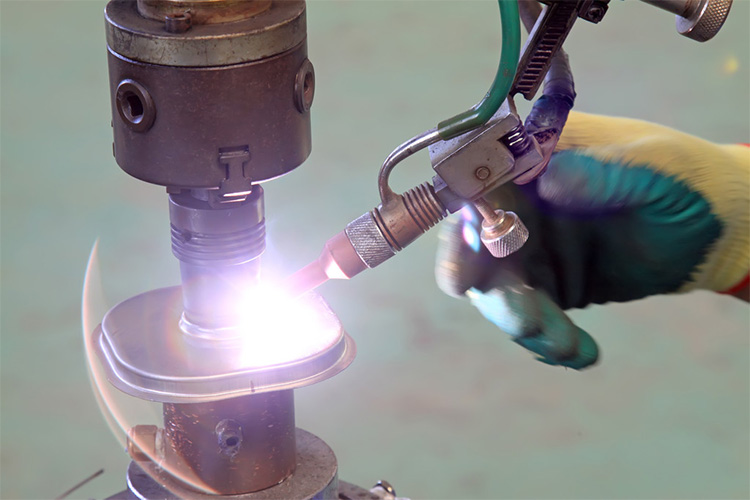

Tungsten electrodes are commonly used in gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW or TIG welding) for their high melting point and stability at high temperatures.
Sporting Goods
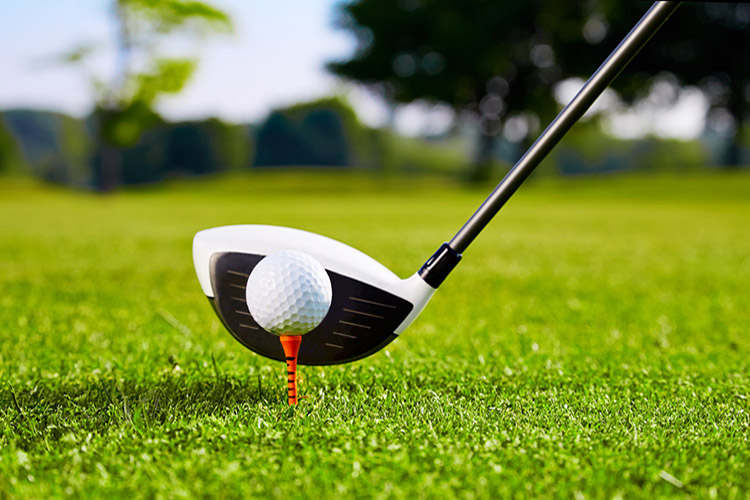

Tungsten alloys are used in the production of darts, golf club heads, and fishing weights due to their high density and small size.
Jewelry and Fashion Accessories
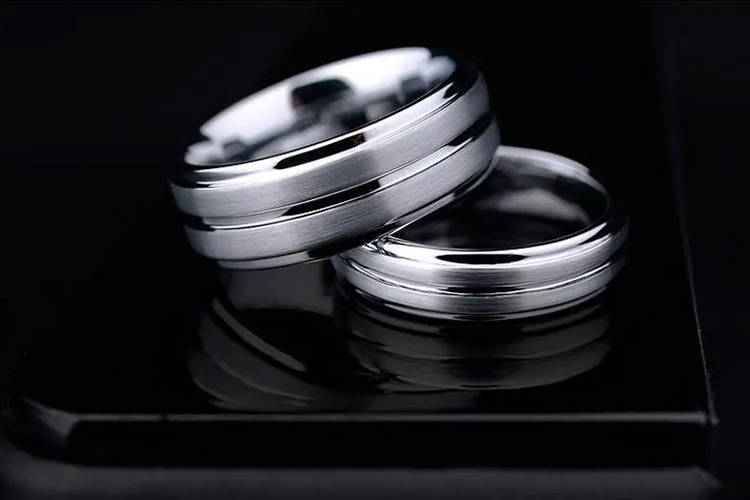

Tungsten carbide is used in the jewelry industry to create durable and scratch-resistant rings and other accessories.
Photovoltaic
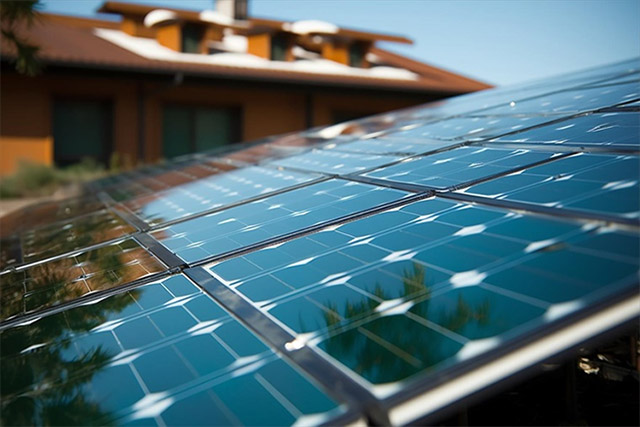

Photovoltaic silicon wafers will develop in the direction of “large size” and “thin wafer” in the future. Under the trend of “thinnerization”, “fine wire and high speed” are the main development trends of diamond wire. Tungsten wire has the advantages of large thin wire space, high tensile strength, strong breaking force, good toughness, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance. It will gradually replace high carbon steel wire and become a new generation of diamond-cutting wire busbar.
Your Comprehensive Guide to Purchasing Tungsten
- Define Your RequirementsMaterial Form: Determine the form of tungsten you need (e.g., bars, sheets, rods, wires, powder). Purity: Specify the required purity level (e.g., 99.95%, 99.99%) based on your application.
- Understand Tungsten GradesFamiliarize yourself with different tungsten grades, such as pure tungsten (W) and tungsten alloys (e.g., WNiFe, WNiCu, WRe, WMo, WCu, AgW, WC).
- Application ConsiderationsConsider the specific application requirements (e.g., high-temperature stability, radiation shielding, electrical conductivity) to choose the most suitable tungsten form and grade.
- Quality StandardsEnsure that the tungsten meets relevant quality standards, such as ASTM specifications for tungsten and tungsten alloys.
- Research SuppliersIdentify reputable tungsten suppliers or manufacturers. Check supplier certifications, quality control processes, and industry reputation.
- Request for Quotations (RFQ)Prepare a detailed RFQ outlining your requirements, including quantity, specifications, delivery timeline, and any specific quality standards.
- Evaluate QuotationsEvaluate received quotations based on factors such as price, lead time, and supplier reputation. Pay attention to any additional services offered by the supplier (e.g., custom machining)
- Material Testing and CertificationRequest information on material testing and certifications to ensure compliance with specified standards.
- Supplier CommunicationEngage in open communication with potential suppliers to clarify any queries and ensure mutual understanding of requirements.Email, call, Whatsapp, Wechat, LinkedIn, skype
- CustomizationIf your application requires specific modifications (e.g., custom shapes, sizes), prepare the the drawings first.
- Shipping and LogisticsConfirm shipping terms, logistics, and packaging methods with the supplier.
Be aware of any import/export regulations and customs requirements. - Payment TermsAgree on payment terms and conditions with the supplier.
Ensure transparency in pricing and any additional costs. - Supplier ReliabilityAssess the supplier’s reliability, on-time delivery track record, and responsiveness to queries.
- Review ContractsReview and formalize contracts, including specifications, quality standards, delivery terms, and payment conditions.
- Continuous CommunicationMaintain ongoing communication with the supplier to address any issues promptly and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Quality Inspection upon ReceiptConduct quality inspections upon receiving the tungsten to verify compliance with specifications and standards.
- DocumentationKeep thorough documentation of the procurement process, including contracts, certificates, and inspection reports.
- Feedback and Continuous ImprovementProvide feedback to the supplier based on your experience.
Use the feedback to improve the procurement process for future purchases.
By following these steps, you can enhance the likelihood of a successful tungsten procurement process that aligns with your specific application needs.