Zirconia Grinding Ball
Zirconia Mortar and Pestle
YSZ Powder
Zirconia Ceramic Parts
Zirconia Powder
Zirconium Nitride Powder
Zirconium Silicate Powder
Fused Zirconia Powder
Zirconium Powder
Zirconium Carbide Powder
Zirconium Foil
Zirconium Plate
ARS- Your Premium Supplier of Zirconium and Zirconium Products
Welcome to ARS, your premier destination for unparalleled zirconium solutions. As a distinguished supplier, we stand at the forefront of the zirconium industry. Our legacy is built on a commitment to precision, quality, and innovation. This ensures that each zirconium product we offer meets the highest industry standards.
ARS has a rich history of expertise. It is dedicated to tailored solutions. We are your trusted partner in meeting the unique demands of your projects. Explore our diverse range of zirconium products, which are backed by rigorous quality assurance and a sustainable approach to production.
Explore Our Zirconium Products
Diverse Range of Zirconium
Our commitment to meeting diverse industry needs is reflected in our extensive array of zirconium products. Whether you’re seeking high-grade zirconium powder, plate, sheet, foil, bar, tube or rod, our catalog offers a comprehensive selection tailored to your specific requirements.
Customized Zirconium Solutions
We collaborate closely with clients to understand your unique demands, offering customized services that ensure each zirconium product aligns perfectly with your project specifications.
-
 Zirconia Powder
Zirconia Powder -
 Zirconium Powder
Zirconium Powder -
 Zirconium Fasteners
Zirconium Fasteners -
 Zirconium Rod
Zirconium Rod -
 Zirconium Sheet
Zirconium Sheet -
 Zirconium Boride Powder
Zirconium Boride Powder -
 Zirconium Sputtering Target
Zirconium Sputtering Target -
 Zirconium Tube & Pipe
Zirconium Tube & Pipe -
 Zirconium Wire
Zirconium Wire -
 Zirconium Bar
Zirconium Bar -
 Zirconium Plate
Zirconium Plate -
 Zirconium Foil & Strip
Zirconium Foil & Strip -
 Zirconium Carbide Powder
Zirconium Carbide Powder -
 Zirconium Powder
Zirconium Powder -
 Fused Zirconia Powder
Fused Zirconia Powder -
 Zirconium Silicate Powder
Zirconium Silicate Powder -
 Zirconium Nitride Powder
Zirconium Nitride Powder -
 Zirconia Ceramic Parts
Zirconia Ceramic Parts -
 Yttria-stabilized Zirconia Powder
Yttria-stabilized Zirconia Powder -
 Zirconia Mortar and Pestle
Zirconia Mortar and Pestle -
 Zirconia Grinding Ball
Zirconia Grinding Ball
Why Choose ARS
With expertise and a reputation for reliability, ARS ensures that every customer receives not just a product, but a solution tailored to your unique needs.
Quality Assurance
We have stringent quality standards which ensure that every piece of zirconium meets industry benchmarks. We also benefit from our rich history of expertise in zirconium processing, production, and quality control.
High Purity Levels
We make sure our zirconium is in its purest form, with products boasting exceptional purity levels that meet the requirements of various industries.
Continuous Innovation
Stay at the forefront of technological advancements in zirconium. We consistently invest in research and development to offer innovative solutions that meet evolving industry needs.
Competitive Pricing
Enjoy cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Our competitive pricing ensures that you receive exceptional value for your investment in zirconium.
Responsive Technical Support
Have technical questions or need assistance? Our dedicated technical support team is ready to provide prompt and comprehensive assistance.
Choose ARS for zirconium products that not only meet but exceed expectations, providing you with a competitive edge and peace of mind in your projects.

Zirconium Properties
| Atomic Number | 40 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Mass | 91.22 g.mol -1 |
| Electronegativity According To Pauling | 1.2 |
| Density | 6.49 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Melting point | 1852 °C |
| Boiling point | 4400 °C |
| Van der Waals Radius | 0.160 nm |
| Ionic Radius | 0.08 nm (+4) |
| Isotopes | 11 |
| Electronic Shell | [ Kr ] 4d2 5s2 |
| Energy of First Ionization | 669 kJ.mol -1 |
| Energy of Second Ionization | 1346 kJ.mol -1 |
| Energy of Third Ionization | 2312 kJ.mol -1 |
| Energy of Fourth Ionization | 3256 kJ.mol -1 |
| Discovered by | Martin Klaproth in 1789 |
Zirconium Applications Across Industries
Zirconium, a durable and adaptable metal, is used in a variety of industries, contributing to technological advancements and innovation. Its unique combination of corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and mechanical strength makes it a sought-after material.

Aerospace
Zirconium, valued for its lightweight and high-temperature stability, is used in the aerospace industry to build aircraft components, jet engines, and spacecraft.

Chemical Processing
Zirconium’s outstanding corrosion resistance makes it ideal for chemical processing applications. This includes the production of pumps, valves, and vessels designed for corrosive environments.

Medical
Zirconium alloys, known for their biocompatibility, are widely used in medical applications such as prosthetic devices and dental implants.
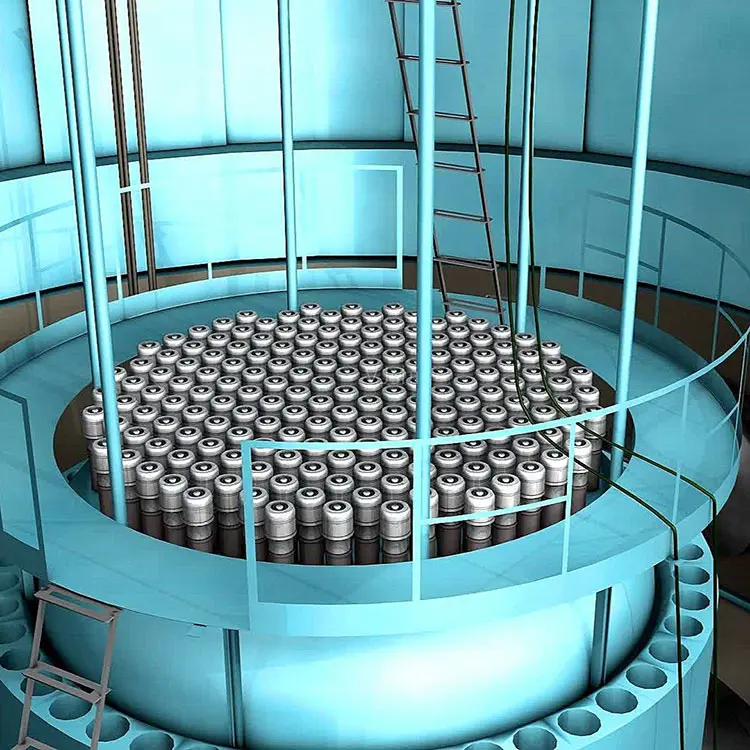
Nuclear Industry
Zirconium’s corrosion resistance and heat tolerance make it vital for cladding fuel rods in nuclear reactors, promoting the safety and efficiency of nuclear power plants.

Automotive
Zirconium is used in the automotive industry due to its corrosion-resistant properties. It’s essential in creating components that withstand harsh conditions, like exhaust systems and catalytic converters.

Oil and Gas
Zirconium’s resistance to corrosion makes it invaluable in the oil and gas industry. It’s used in equipment and parts that face corrosive conditions during extraction, refining, and transportation.

Textile
Zirconium compounds are used in the textile industry as catalysts in the production of synthetic fibers and other textile materials.

Ceramics
Zirconium compounds are integral to the ceramics industry, enhancing the production of high-performance ceramics for diverse applications such as cutting tools and refractory materials.
Make Zirconium And Its Products
Zirconium, a remarkable metal known for its exceptional properties, undergoes a detailed and sophisticated process to transform from raw materials into the diverse range of high-quality products that contribute to various industries.
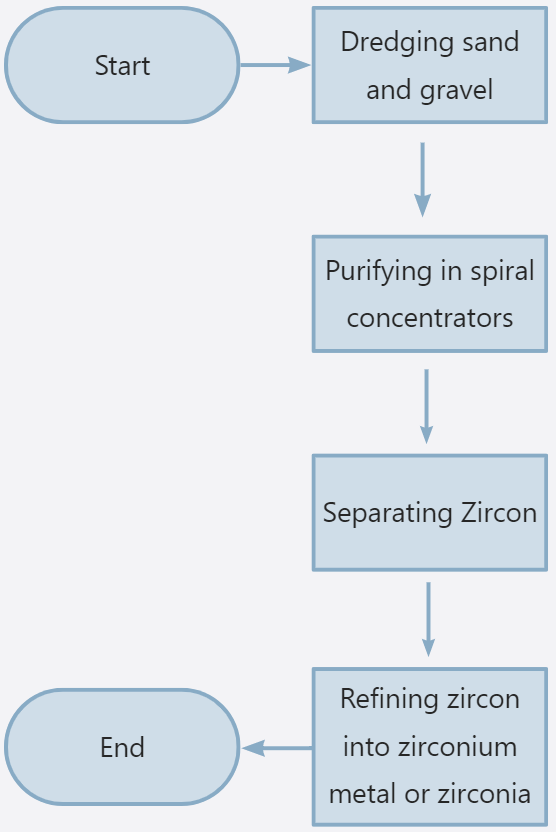
The process typically begins with the extraction of zirconium-containing minerals, and zircon is a primary source. The sand and gravel that contain zircon are typically collected from coastal waters by a floating dredge, a large steam shovel fitted on a floating barge. After the shovel has scooped up the gravel and sand, they are purified by means of spiral concentrators, and then unwanted material is removed by magnetic and electrostatic separators.
End-product manufacturers of zircon further refine the nearly pure zircon into zirconium by using chlorine to purify the metal and then sintering(heating) it until it becomes sufficiently workable for industrial use. Less-pure zircon is made into zirconia, an oxide of zirconium, by fusing the zircon with coke, iron borings, and lime until the silica is reduced to silicon that alloys with the iron.
Following the production of zirconium metal, it is further processed into various forms such as bars, sheets, powders, and alloys. Each form undergoes specific manufacturing processes tailored to its intended application.
Zirconium Bar
Melting and Casting: The zirconium metal produced from reduction undergoes a melting process. The molten zirconium is then cast into ingots or molds to form solid bars.
Hot Working: The cast zirconium bars may undergo hot working processes such as extrusion or forging to achieve the desired shape and dimensions.
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment is applied to optimize the microstructure and mechanical properties of the zirconium bars. This step ensures enhanced strength and other desired characteristics.
Surface Finishing: Zirconium bars may undergo surface finishing processes, such as polishing or machining, to meet specific surface requirements.
Zirconium Sheet
Rolling: Zirconium sheets are typically produced through rolling processes. The zirconium metal is passed through rolling mills to reduce thickness and achieve the desired sheet dimensions.
Annealing: Annealing processes may be applied to relieve stress and enhance the material’s ductility. This step ensures the zirconium sheets maintain their integrity during further processing.
Cutting and Shearing: The rolled and annealed zirconium sheets are cut and sheared to the required size and shape.
Surface Treatment: Surface treatment methods, such as pickling or passivation, may be employed to enhance the corrosion resistance of zirconium sheets.
Zirconium Powder
Hydriding/Dehydriding Process: Zirconium sponge is subjected to a hydriding process, where it absorbs hydrogen, causing it to become brittle.The hydrided zirconium is then mechanically processed to create fine zirconium powder. Dehydriding follows to remove the absorbed hydrogen.
Sizing and Classification: The zirconium powder is sized and classified to achieve the desired particle size distribution.
Quality Control
The quality control methods implemented in the production of zirconium metal are typical Statistical Process Control (SPC) methods used in most metal production. These involve tracking and controlling specific variables determined by the end product requirements. Stringent government quality control is applied to all zirconium metal produced for nuclear applications. These controls assure that the zirconium produced for use in a nuclear plant has been processed correctly and also allow for accountability: processing is tracked so that it can be traced back to each individual step and location.
Quality control methods for zirconium used in refractory applications also focus on SPC. However, in the refractory industries, it is also necessary to ascertain the beach (and even what part of the beach) from which the zirconium mineral was extracted. We would specify the source of the zirconium because each source contains slightly different trace elements, and different trace elements can affect the final product.
Guide for purchasing Zirconium

Talk to Our Expert
Define Your Requirements
Identify the specific application and requirements for the zirconium product. Consider factors such as size, form (bars, sheets, powders), purity, and any special characteristics needed.
Customization Options
If your project requires specific features, a supplier with flexible manufacturing capabilities can tailor zirconium products to meet your unique specifications.
Assess Quality Standards
Industry standards and relevant certifications should be followed. You can request detailed information on the testing and inspection processes applied to zirconium products.
Price and Delivery
Ensure transparency in pricing and inquire about any additional fees or charges. Timely delivery is crucial, so clarify shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and the supplier’s ability to meet your project timeline.
Technical Expertise and Customer Support
Leverage our technical expertise and dedicated customer support. We’re here to assist with technical queries, guide you in product selection, and provide ongoing support post-purchase.
Quality Control:
Rigorous quality control measures, including particle size and purity testing, ensure the zirconium powder meets specified standards.
Zirconium Alloys
Alloying Process: Additional alloying elements, such as niobium or tin, are introduced during the melting process. This step forms zirconium alloys with specific properties tailored to the intended application.
Casting or Forming: The molten zirconium alloy is cast into the desired shape or formed through processes like extrusion or forging.
Heat Treatment: Zirconium alloys undergo heat treatment to refine their microstructure and enhance mechanical properties.
Final Inspection: Zirconium alloys undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet stringent quality standards before being prepared for distribution.